Small manufacturing businesses are the backbone of many economies, driving innovation and providing essential goods. However, operating in this dynamic environment comes with its own set of challenges, often involving intense competition, tight margins, and the constant pressure to deliver more with less. In this landscape, the quest for efficiency isn’t just a goal; it’s a survival imperative. This article will delve deep into how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, transforming their operations from reactive to proactive, and paving the way for sustainable growth.
1. The Efficiency Imperative for Small Manufacturers
For countless small manufacturing businesses, the daily grind often involves juggling multiple tasks, managing disparate systems, and making critical decisions based on fragmented information. From tracking raw materials to overseeing production lines and handling customer orders, the sheer volume of operational data can be overwhelming. Without a cohesive system, bottlenecks emerge, errors proliferate, and valuable time and resources are squandered. The imperative to become more efficient isn’t merely about cutting costs; it’s about enhancing responsiveness, improving product quality, and ultimately, staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Many small manufacturers find themselves stuck in a cycle of manual processes and outdated spreadsheets, which, while seemingly cost-effective in the short term, are actually silently eroding their profit margins and hindering their ability to scale. These methods are prone to human error, difficult to update in real-time, and offer very little in the way of comprehensive insights into the overall health and performance of the business. Recognising this need for transformation, many forward-thinking entrepreneurs are now exploring technological solutions, specifically asking: how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses and provide a pathway to a more streamlined and profitable future?
2. Understanding the Unique Challenges of Small Manufacturing Businesses
Small manufacturing enterprises, despite their agility and niche focus, face a distinct set of hurdles that can impede their growth and operational fluidity. Unlike their larger counterparts, they often operate with limited budgets, fewer personnel, and less access to advanced technologies. This often means that critical functions, such as inventory management, production scheduling, and financial tracking, are handled in silos, leading to data inconsistencies and a lack of integrated oversight. The absence of a unified system makes it incredibly difficult to get a holistic view of operations, leading to delays, miscommunications, and missed opportunities.
Furthermore, these businesses frequently struggle with unpredictable demand fluctuations, the complexities of supply chain management, and the constant pressure to meet tight deadlines while maintaining high-quality standards. Managing raw material procurement, work-in-progress, and finished goods inventory accurately is a monumental task when relying on manual counts or disconnected spreadsheets. The lack of real-time visibility into these processes means that stockouts can halt production, or conversely, overstocking can tie up valuable capital. Addressing these foundational challenges is precisely where the strategic implementation of an ERP system begins to make a profound difference, illustrating how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses by tackling these core pain points head-on.
3. What Exactly is an ERP Solution and Why Does It Matter?
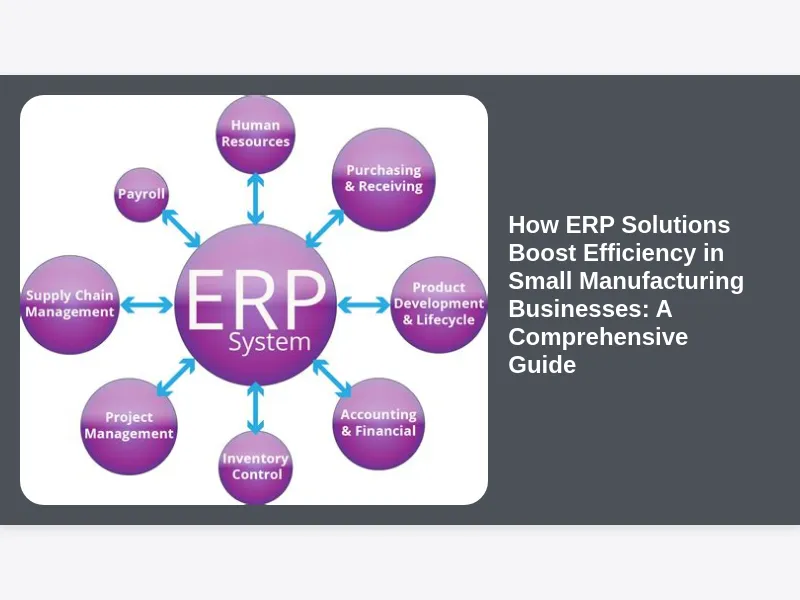
At its core, an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solution is a comprehensive software system designed to integrate and manage all the essential functions of an enterprise, from finance and human resources to manufacturing and supply chain operations, all within a single, unified database. Imagine a central nervous system for your business, where every piece of information, every transaction, and every process is interconnected and accessible in real-time. This integration eliminates the need for separate systems for different departments, fostering seamless communication and data flow across the entire organization.
For small manufacturing businesses, an ERP system isn’t just a fancy piece of software; it’s a strategic asset that brings order to chaos. It consolidates critical business data, providing a single source of truth that all departments can rely upon. This means that financial data, production schedules, inventory levels, sales orders, and customer information are all updated simultaneously, offering an accurate and up-to-the-minute picture of the business. By breaking down departmental silos and fostering a collaborative environment, ERP truly demonstrates how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, transforming disparate functions into a cohesive, high-performing unit ready to adapt and grow.
4. How ERP Solutions Boost Efficiency in Small Manufacturing Businesses Through Centralized Data
The cornerstone of an ERP system’s ability to drive efficiency lies in its capacity to centralize all operational data. Prior to ERP, it was common for departments to maintain their own databases and spreadsheets – sales had one, production another, and finance a third. This often led to inconsistencies, duplicate data entry, and a significant amount of time spent reconciling discrepancies, rather than focusing on value-added activities. Such fragmentation invariably creates delays and makes informed decision-making a frustrating, if not impossible, endeavor for small manufacturers.
With an ERP solution, all vital information, from raw material stock levels to customer order details and financial transactions, resides in a single, integrated database. This “single source of truth” ensures that everyone in the organization is working with the most current and accurate information. When a sales order is placed, inventory is updated, production schedules are adjusted, and financial records are prepared, all automatically and in real-time. This eliminates redundant data entry, reduces the likelihood of errors, and dramatically speeds up information flow, which is a prime example of how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses by providing unparalleled data coherence and accessibility.
The immediate benefit of this centralized data approach is a significant reduction in administrative overhead and a marked improvement in operational accuracy. Imagine the time saved when your sales team can instantly see current stock levels and production lead times, providing accurate delivery estimates to customers without needing to call the warehouse or production floor. Similarly, your finance department gains real-time insight into costs, revenues, and inventory valuations, making financial reporting and analysis much more straightforward and reliable. This foundational shift in data management is precisely what empowers small manufacturing businesses to operate with a new level of precision and speed, showcasing the transformative power of ERP.
5. Streamlining Inventory Management and Reducing Waste
One of the most significant drains on efficiency and profitability for small manufacturers is poor inventory management. Holding too much stock ties up capital, incurs storage costs, and increases the risk of obsolescence or damage. Conversely, holding too little stock leads to production delays, missed sales opportunities, and dissatisfied customers. Manually tracking inventory or relying on basic spreadsheets often results in inaccurate stock counts, leading to either overstocking or painful stockouts. This constant struggle to balance inventory levels directly impacts the bottom line and operational flow.
ERP solutions revolutionize inventory management by providing real-time visibility into every item in your warehouse, from raw materials to work-in-progress and finished goods. The system tracks items as they move through the supply chain, from receipt to dispatch, automatically updating stock levels with every transaction. This precision allows for more accurate demand forecasting, enabling businesses to order just what they need, exactly when they need it. By optimizing inventory levels, ERP systems help small manufacturing businesses reduce carrying costs, minimize waste from obsolete stock, and avoid costly production stoppages due to material shortages.
Furthermore, an ERP system can implement strategies like just-in-time (JIT) inventory, where materials arrive precisely when they are needed for production, further minimizing storage costs and waste. It can also help identify slow-moving or obsolete inventory, allowing businesses to take corrective action before these items become a complete loss. This proactive approach to inventory control is a critical aspect of how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, directly translating into significant cost savings, improved cash flow, and a more agile response to market demands.
6. Optimizing Production Planning and Scheduling for Agility
The production floor is the heart of any manufacturing business, and its efficiency directly impacts profitability and delivery timelines. Small manufacturers often grapple with complex production schedules, machine breakdowns, workforce availability, and material shortages, making the planning process a constant battle. Manual scheduling methods are prone to errors, difficult to adjust on the fly, and often fail to account for the intricate interdependencies between different production stages. This lack of dynamic planning leads to underutilized machinery, idle workers, and delayed customer orders.
An ERP system brings sophisticated production planning and scheduling capabilities within reach of small manufacturers. It integrates seamlessly with inventory and sales data, allowing for realistic production plans that consider available materials, machine capacity, and labor resources. The system can generate detailed production schedules, optimize batch sizes, and even suggest alternative routing if a particular machine is down or a material is delayed. This level of foresight and adaptability transforms the production process from a reactive scramble into a well-orchestrated operation.
Moreover, ERP enables businesses to respond swiftly to changes in customer demand or unforeseen disruptions. If an urgent order comes in, the system can quickly assess its impact on the existing schedule and suggest the most efficient way to incorporate it without jeopardizing other commitments. This agility in production planning not only improves on-time delivery rates but also maximizes the utilization of resources, reducing operational costs and enhancing throughput. This optimization of the manufacturing process is a powerful demonstration of how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, empowering them to be more responsive and productive than ever before.
7. Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility and Collaboration
For small manufacturing businesses, the supply chain is a complex web of suppliers, logistics providers, and customers, often extending globally. Lacking comprehensive visibility into this network can lead to numerous inefficiencies: delays in material deliveries, unexpected price fluctuations, quality issues from suppliers, and a general inability to react quickly to disruptions. Without integrated tools, communicating with suppliers, tracking inbound shipments, and monitoring vendor performance becomes a laborious and often fragmented process, leaving businesses vulnerable to unforeseen challenges.
An ERP solution acts as a central hub for supply chain management, pulling together data from various points to provide end-to-end visibility. It integrates supplier information, purchase orders, shipping manifests, and inventory movements into a single view. This means you can track the status of raw materials from the moment they leave your supplier’s facility until they arrive at your dock, and beyond, into your production process. This enhanced visibility allows small manufacturers to anticipate potential delays, proactively address issues, and make more informed decisions regarding sourcing and logistics.
Beyond mere visibility, ERP fosters better collaboration with supply chain partners. By providing suppliers with access to relevant data – such as forecasted demand or current inventory levels – businesses can work more closely to optimize delivery schedules and reduce lead times. Similarly, sharing production and shipping updates with customers can significantly improve satisfaction. This integrated approach to supply chain management minimizes risks, reduces the impact of disruptions, and ultimately ensures a smoother, more reliable flow of materials and products, which is a key aspect of how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses by strengthening their entire operational ecosystem.
8. Improving Quality Control and Compliance
Maintaining high product quality is paramount for any manufacturing business, especially for small enterprises looking to build a strong reputation and customer loyalty. However, managing quality control manually or through fragmented systems can be incredibly challenging. Tracking defects, identifying their root causes, and ensuring adherence to industry standards and regulatory compliance often involves extensive paperwork, disconnected inspection processes, and a reactive approach to quality issues. This can lead to costly rework, customer returns, and potential fines for non-compliance.
ERP solutions can integrate quality control processes directly into the manufacturing workflow, transforming it from an afterthought into an intrinsic part of operations. The system can enforce quality checks at various stages of production, from incoming raw materials inspection to in-process checks and final product testing. If a quality issue is detected, the ERP can trigger alerts, initiate corrective actions, and track the resolution process, creating a comprehensive audit trail. This proactive approach helps identify and address quality problems early, reducing waste and preventing defective products from reaching customers.
Furthermore, ERP systems are invaluable for managing compliance with industry-specific regulations and certifications. They can store and manage documentation, track revision histories, and ensure that all processes adhere to required standards. For instance, in industries with strict regulatory requirements, an ERP can ensure that all production steps are recorded and traceable, simplifying audits and demonstrating compliance. This robust approach to quality and compliance is a crucial element in understanding how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, safeguarding their reputation, reducing liabilities, and ensuring a consistently high standard of output.
9. Gaining Real-time Insights for Better Decision-Making
In the fast-paced world of small manufacturing, quick and informed decision-making is a significant competitive advantage. However, when data is scattered across various departments and systems, extracting meaningful insights becomes a time-consuming and often retrospective exercise. Business owners and managers frequently find themselves relying on gut feelings or outdated reports, which can lead to missed opportunities, poor resource allocation, and a slow response to market changes or operational issues. This lack of immediate, comprehensive data can severely hinder agility and strategic planning.
An ERP system centralizes all operational and financial data, making it possible to generate real-time reports and dashboards that provide an up-to-the-minute view of the business. From sales performance and inventory levels to production costs and delivery metrics, managers can access key performance indicators (KPIs) at a glance. This immediate access to accurate data empowers decision-makers to identify trends, pinpoint inefficiencies, and proactively address problems as they arise, rather than discovering them weeks or months later.
For example, a sudden dip in production efficiency can be immediately flagged, allowing managers to investigate and resolve the issue before it significantly impacts order fulfillment. Similarly, real-time sales data can inform marketing strategies or trigger adjustments in production schedules. This capacity for instant insight is a fundamental aspect of how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, transforming decision-making from an art into a science, and providing the clarity needed to navigate complex challenges and capitalize on new opportunities with confidence.
10. Automating Financial Operations and Reducing Manual Errors
Financial management is the backbone of any business, but for small manufacturers, it often involves a tedious and error-prone process of manual data entry, reconciliation of disparate accounts, and generation of complex reports. Tracking costs across different production runs, managing accounts payable and receivable, and generating accurate financial statements can consume an enormous amount of time and resources. Errors in financial data can have significant consequences, leading to inaccurate forecasting, compliance issues, and ultimately, poor business decisions.
ERP solutions seamlessly integrate financial modules with other operational functions like sales, procurement, and production. This integration means that every transaction – from a raw material purchase to a finished goods sale – automatically updates the general ledger. This eliminates the need for manual data entry into separate accounting software, significantly reducing the risk of human error and ensuring that financial records are always current and accurate. Accounts payable and receivable processes are streamlined, with automated invoicing, payment tracking, and reconciliation, improving cash flow management.
Furthermore, an ERP system can provide granular cost accounting, allowing small manufacturers to precisely track the costs associated with each product, production run, or customer order. This detailed cost visibility is invaluable for pricing strategies, identifying areas for cost reduction, and understanding true profitability. Automated financial reporting generates balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow reports on demand, providing a clear and comprehensive picture of the company’s financial health. This level of automation and accuracy in financial operations is a compelling example of how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, freeing up valuable resources and providing unparalleled financial transparency.
11. Scaling Your Operations with a Future-Proof ERP System
Growth is the ambition of most small manufacturing businesses, but scaling operations effectively without the right infrastructure can quickly lead to disorganization and new inefficiencies. As production volumes increase, customer bases expand, and new product lines are introduced, manual processes and fragmented systems quickly become bottlenecks. What worked for a handful of orders a day simply won’t suffice for hundreds, making sustained growth a daunting prospect unless the underlying operational framework is robust enough to support it.
An ERP system provides the scalable foundation that small manufacturers need to grow confidently. Designed to handle increasing volumes of data and transactions, an ERP can adapt as your business evolves. Whether you’re adding new production lines, expanding into new markets, or hiring more employees, the system can be configured to accommodate these changes without requiring a complete overhaul of your IT infrastructure. Its modular nature often means you can add new functionalities or modules as your business needs grow, ensuring that your investment continues to deliver value over time.
This inherent scalability means that a well-implemented ERP system is not just a solution for today’s problems, but an investment in the future. It allows your business to maintain efficiency and control even as it expands in complexity and size. Without the need to constantly replace or integrate new standalone software, you save significant time and resources in the long run. This forward-looking capability is a testament to how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, providing a stable and adaptable platform that empowers them to embrace growth without fear of outgrowing their operational capabilities.
12. The Implementation Journey: What Small Businesses Should Expect
Embarking on an ERP implementation journey can seem like a significant undertaking for small manufacturing businesses, often raising concerns about disruption, cost, and complexity. However, understanding the typical phases involved can demystify the process and help set realistic expectations. The journey usually begins with a thorough planning phase, where the business defines its specific needs, objectives, and identifies the key pain points the ERP is intended to address. This initial stage is crucial for selecting the right ERP vendor and solution that aligns with the company’s size, industry, and budget.
Following selection, the implementation proceeds with data migration, where existing information from various legacy systems is carefully transferred into the new ERP. This can be one of the most time-consuming steps, requiring meticulous attention to data quality and accuracy to ensure the new system operates flawlessly. Concurrently, the ERP system is configured to match the specific workflows and business rules of the manufacturing operation. This often involves customizing settings, defining user roles, and setting up reports that are relevant to the business.
Finally, user training and go-live are critical stages where employees learn to navigate and utilize the new system effectively. A successful implementation culminates in the system going live, followed by a period of post-implementation support and optimization to fine-tune performance and address any unforeseen issues. While challenging, navigating this journey effectively is how small manufacturers unlock the full potential of how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, ensuring a smooth transition to integrated operations and a strong return on their investment.
13. Measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of ERP for Small Manufacturers
For any significant business investment, especially one as comprehensive as an ERP system, understanding the return on investment (ROI) is crucial. Small manufacturing businesses need to clearly articulate the tangible and intangible benefits to justify the initial outlay of time and capital. While some benefits, like reduced inventory costs or improved on-time delivery, are straightforward to quantify, others, such as enhanced decision-making or improved employee morale, are equally important but harder to put a precise number on.
Quantifiable ROI often stems from several key areas. These include reductions in operational costs through optimized inventory, streamlined production, and automated administrative tasks. Businesses frequently see a decrease in labor costs associated with manual data entry and reconciliation, and a significant reduction in errors leading to less rework and fewer warranty claims. Improved cash flow from faster invoicing and payment cycles also contributes directly to the bottom line. It’s not uncommon for companies to experience significant savings within the first few years, making a compelling case for the financial viability of ERP.
Beyond the direct financial gains, the strategic ROI is equally compelling. Enhanced customer satisfaction due to improved order accuracy and faster delivery, the ability to scale operations without proportional increases in overhead, and a clearer, real-time view of business performance all contribute to long-term success. By carefully tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) before and after implementation, small manufacturing businesses can empirically demonstrate how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, not just in terms of operational smoothness but also in terms of measurable financial and strategic gains that drive sustainable growth.
14. Cloud-Based ERP: A Game-Changer for Accessibility and Affordability
Historically, ERP systems were large, complex, and required significant upfront investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure, often putting them out of reach for small manufacturing businesses. The advent of cloud-based ERP, often referred to as SaaS (Software as a Service) ERP, has dramatically changed this landscape, making these powerful solutions accessible and affordable to a much broader range of enterprises. Cloud ERP operates over the internet, with the software and data hosted by the vendor, eliminating the need for on-premise servers and dedicated IT staff.
This model offers several compelling advantages for small manufacturers. Firstly, the financial barrier to entry is significantly lowered. Instead of large capital expenditures, businesses typically pay a subscription fee, transforming a large upfront cost into predictable operational expenses. This subscription often includes software updates, maintenance, and support, further reducing the total cost of ownership. Secondly, cloud ERP offers unparalleled accessibility, allowing authorized users to access the system from anywhere, at any time, on any device with an internet connection. This flexibility is invaluable for remote teams, mobile salesforces, and owners who need to monitor operations while off-site.
Furthermore, cloud providers typically offer robust security measures, data backup, and disaster recovery, which small businesses might struggle to implement and maintain on their own. The scalability of cloud solutions also means that as a business grows, its ERP system can easily scale up or down to meet changing demands without major infrastructure changes. This combination of lower cost, greater accessibility, enhanced security, and inherent scalability clearly illustrates how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses by making advanced technology achievable and manageable, democratizing sophisticated operational control.
15. Customization vs. Out-of-the-Box: Finding the Right Fit for Your Business
When considering an ERP solution, small manufacturing businesses often face the dilemma of choosing between a highly customized system tailored to their unique processes or an out-of-the-box solution with standard functionalities. Each approach has its merits and drawbacks, and the optimal choice largely depends on the specific needs, complexity, and budget of the individual business. Understanding this trade-off is critical to selecting an ERP that genuinely boosts efficiency rather than introducing unnecessary complications.
An out-of-the-box ERP offers a standardized set of features and workflows that are typically best practices across various industries. This approach usually leads to faster implementation, lower initial costs, and easier upgrades, as the system isn’t heavily modified. For many small manufacturers with relatively straightforward processes, an out-of-the-box solution, possibly with minor configurations, can be highly effective. It allows them to leverage proven methodologies and quickly realize the benefits of integration and automation, demonstrating how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses without excessive complexity.
Conversely, a highly customized ERP is built or heavily modified to precisely match a business’s unique operational requirements. This might be necessary for manufacturers with highly specialized production processes, unique compliance needs, or proprietary workflows that offer a significant competitive advantage. While customization can provide an exact fit, it often comes with higher costs, longer implementation times, and potentially more challenging upgrades. A balanced approach often involves selecting an ERP that offers a solid core of functionality and allows for configuration rather than extensive coding, ensuring flexibility without sacrificing the benefits of standardization, making it a powerful tool for tailored efficiency.
16. Training and User Adoption: Ensuring Your Team Embraces the Change
Implementing an ERP system is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a significant organizational change. Even the most sophisticated ERP solution will fail to deliver its promised efficiency gains if employees are not adequately trained or are resistant to adopting the new system. User adoption is a critical success factor, as the system’s effectiveness is directly proportional to how well and how consistently it is used by the people who operate it daily. Overlooking this human element can undermine the entire investment.
Effective training programs are paramount. They should not only cover the technical aspects of using the ERP software but also explain the “why” behind the change – how the new system will benefit individual roles, streamline tasks, and ultimately contribute to the company’s success. Training should be tailored to different user groups (e.g., finance, production, sales) focusing on the modules and functionalities most relevant to their daily responsibilities. Hands-on exercises, clear documentation, and ongoing support are essential components of a successful training strategy.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of acceptance and championing the new system from leadership can significantly boost user adoption. When employees feel supported, understand the benefits, and are given the tools to succeed, they are more likely to embrace the change and leverage the ERP to its full potential. This comprehensive approach to training and change management is key to ensuring how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses is realized through enthusiastic and proficient user engagement, turning potential resistance into genuine empowerment.
17. Overcoming Common Pitfalls in ERP Adoption
While the benefits of ERP for small manufacturing businesses are clear, the adoption journey is not without its potential pitfalls. Acknowledging and proactively addressing these common challenges can significantly improve the chances of a successful implementation and ensure the desired efficiency gains are achieved. One of the most frequent issues is inadequate planning, where businesses rush into selecting a system without thoroughly understanding their own needs, processes, and long-term objectives. This can lead to choosing a solution that is either too complex or lacks critical functionality.
Another significant pitfall is insufficient budget allocation, not just for the software itself, but also for implementation services, data migration, training, and ongoing support. Underestimating these costs can lead to project delays or, worse, a partially implemented system that fails to deliver full value. Resistance to change from employees, as discussed previously, can also derail an implementation if not managed with clear communication and comprehensive training. People naturally resist what they don’t understand or perceive as a threat to their job security or established routines.
Finally, poor data quality and lack of executive sponsorship are also major hurdles. Migrating dirty or inaccurate data into a new ERP system will only perpetuate existing problems, leading to a “garbage in, garbage out” scenario. Strong leadership and consistent advocacy from the top are essential to maintaining momentum, resolving conflicts, and ensuring that the entire organization remains committed to the project. By anticipating and mitigating these common challenges, small manufacturers can navigate their ERP adoption more smoothly, ensuring that how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses becomes a tangible reality rather than an elusive goal.
18. Beyond Efficiency: Strategic Advantages of ERP for Competitive Edge
While the primary focus of an ERP implementation is often on boosting operational efficiency, the strategic advantages it confers can be just as, if not more, impactful for small manufacturing businesses seeking a competitive edge. In a marketplace increasingly defined by speed, innovation, and customer-centricity, having a robust and integrated system goes beyond merely streamlining processes; it empowers businesses to outperform their rivals and establish a stronger market position.
One significant strategic advantage is enhanced agility and responsiveness to market changes. With real-time data and integrated processes, small manufacturers can quickly identify new market trends, adapt production schedules to meet shifting demand, and even pivot their product offerings more rapidly than competitors relying on outdated systems. This ability to react quickly to both threats and opportunities can be a game-changer. Furthermore, improved data analytics capabilities enable businesses to better understand customer behavior, identify profitable segments, and tailor products or services more effectively, leading to increased customer loyalty and market share.
Moreover, an ERP system strengthens compliance and risk management, which is a significant strategic advantage in today’s regulatory environment. By embedding quality control and compliance measures directly into workflows, businesses can avoid costly penalties, maintain a strong reputation, and confidently expand into new markets with stringent requirements. Ultimately, an ERP doesn’t just make a business run better; it makes it smarter, more resilient, and better positioned for long-term strategic success, illustrating how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses while simultaneously building a foundation for sustainable competitive advantage.
19. Choosing the Right ERP Partner and Solution
The success of an ERP implementation hinges significantly on selecting the right ERP solution and, crucially, the right implementation partner. For small manufacturing businesses, this decision is particularly weighty, given limited resources and the desire to maximize ROI. It’s not just about finding software with a list of features, but about identifying a comprehensive solution that aligns with specific industry needs, business size, growth aspirations, and budget constraints.
The selection process should begin with a thorough internal assessment of current pain points, future goals, and unique operational requirements. This clarity will guide the search for ERP vendors that specialize in manufacturing, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Look for solutions that offer core manufacturing functionalities such as production planning, inventory management, quality control, and shop floor control, alongside essential financial and CRM capabilities. Consider whether a cloud-based solution is more suitable than on-premise, evaluating factors like cost, accessibility, and IT resource availability.
Equally important is the choice of an implementation partner. This partner should possess deep industry expertise in manufacturing, a proven track record with businesses of your size, and a strong understanding of the chosen ERP solution. They should offer comprehensive support from planning and configuration to data migration, training, and post-implementation assistance. A good partner will act as a trusted advisor, guiding you through the complexities and ensuring that the project stays on track and within budget. This thoughtful approach to vendor and partner selection is paramount to truly realizing how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, transforming a significant investment into a powerful catalyst for growth and operational excellence.
20. Conclusion: Empowering Small Manufacturing for a More Efficient Future
In the dynamic and competitive landscape of modern manufacturing, efficiency is no longer a luxury but a fundamental necessity for survival and growth, especially for small businesses. The journey to operational excellence, while challenging, is undeniably achievable with the right strategic tools. Throughout this comprehensive exploration, we’ve unpacked the myriad ways how ERP solutions boost efficiency in small manufacturing businesses, transforming every facet of their operations from fragmented and manual to integrated and automated.
From centralizing critical data and streamlining inventory to optimizing production planning, enhancing supply chain visibility, and automating financial operations, an ERP system provides the foundational infrastructure necessary for a modern, agile manufacturing enterprise. It empowers better, real-time decision-making, improves product quality, ensures compliance, and critically, offers the scalability required to support future growth without the burden of outmoding systems.
The advent of cloud-based ERP has further democratized access to this transformative technology, making it more affordable and accessible than ever before. While the implementation journey requires careful planning, dedicated resources, and a commitment to user adoption, the long-term benefits in terms of cost savings, increased productivity, enhanced customer satisfaction, and a robust competitive edge are undeniable. For small manufacturing businesses ready to shed the limitations of outdated processes and embrace a future of streamlined, intelligent operations, an ERP solution is not just an investment in software; it’s an investment in a more efficient, resilient, and prosperous future.