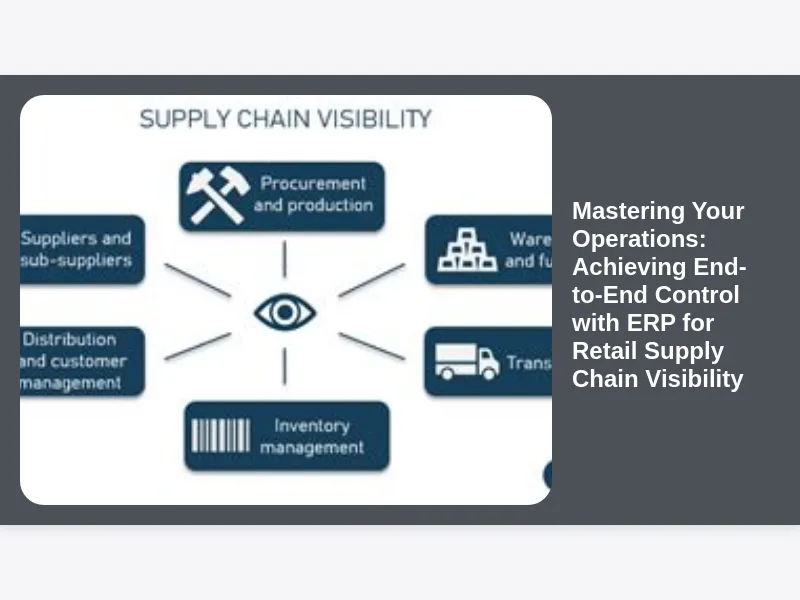
In today’s fast-paced retail landscape, the ability to see clearly across every facet of your operations isn’t just an advantage—it’s a necessity. From the moment raw materials are sourced to the final delivery of a product into a customer’s hands, a myriad of complex processes are at play. Without a unified view, retailers are left navigating a dense fog of uncertainty, making informed decisions nearly impossible. This is precisely where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems step in, offering a transformative solution to gain unprecedented clarity and command. Our journey today explores how a robust ERP system can be your guiding light, ultimately achieving end-to-end control and revolutionizing ERP for retail supply chain visibility.
The Unseen Challenges: Why Retail Supply Chains Struggle with Visibility
Before we delve into the solutions, it’s crucial to understand the inherent complexities that plague traditional retail supply chains. Many retailers operate with fragmented systems, a patchwork of legacy software, spreadsheets, and manual processes that simply don’t communicate with one another. This disjointed environment creates significant blind spots, making it incredibly difficult to track inventory, forecast demand accurately, or even understand the true cost of goods sold. The ripple effects of these challenges are felt throughout the entire organization, impacting everything from customer satisfaction to profitability.
Consider the common scenario: a customer orders an item online, only for the retailer to discover it’s out of stock in their primary warehouse, despite the system showing available units. This discrepancy often stems from delays in data updates between the e-commerce platform, the warehouse management system, and the inventory control module. Such a lack of real-time information leads to cancelled orders, frustrated customers, and ultimately, damaged brand reputation. These operational inefficiencies aren’t just minor inconveniences; they are substantial barriers to growth and sustainability in a competitive market.
Furthermore, managing returns, a critical aspect of modern retail, becomes an absolute nightmare without proper visibility. The journey of a returned item—from customer initiation to inspection, restocking, or disposal—is often opaque. This obscurity leads to lost products, delays in processing refunds, and inaccurate inventory counts, creating financial drains and further exasperating customers. The absence of a single source of truth for all supply chain activities breeds chaos, making it nearly impossible for retailers to respond effectively to market changes or customer demands.
The global nature of today’s supply chains adds another layer of complexity. Retailers often source products from multiple vendors across different continents, each with their own unique logistics and shipping procedures. Tracking these diverse shipments, managing customs, and ensuring timely delivery requires an integrated approach that standalone systems simply cannot provide. Without a consolidated view, delays go unnoticed until it’s too late, leading to stockouts, missed sales opportunities, and a constant scramble to fulfill orders. This fragmented landscape underscores the urgent need for a unified platform that can bring all these disparate elements under one coherent umbrella.
Understanding ERP: The Backbone for Retail Supply Chain Optimization
At its core, an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a comprehensive software solution designed to integrate and manage all the essential business processes of an organization. Think of it as the central nervous system for your entire retail operation, where data from various departments—from finance and human resources to inventory and sales—flows into a single, unified database. This consolidation eliminates data silos, providing a consistent and accurate view of information across the enterprise. For retailers, this means a significant shift from reactive problem-solving to proactive strategic planning.
An ERP system typically comprises multiple integrated modules, each designed to handle specific business functions. For a retail supply chain, these modules might include inventory management, procurement, order processing, warehouse management, logistics, and even customer relationship management (CRM). The magic happens when these modules communicate seamlessly, sharing data in real-time. This interconnectedness allows a purchase order initiated by the procurement team to instantly update inventory levels, inform the finance department, and prepare the warehouse for an incoming shipment, all within the same system.
The true power of ERP lies in its ability to standardize processes and enforce best practices across the organization. By centralizing data and workflows, ERP helps retailers streamline operations, reduce manual errors, and improve overall efficiency. Instead of disparate teams working in isolation, an ERP system fosters collaboration, ensuring that everyone is working from the same playbook and with the most up-to-date information. This harmonization is fundamental for retail supply chain optimization, enabling businesses to move with greater agility and precision in a dynamic market.
Beyond mere data integration, modern ERP systems often incorporate advanced analytics and reporting capabilities. This allows retailers to extract meaningful insights from the vast amounts of data collected, identifying trends, predicting future demand, and pinpointing areas for improvement. By leveraging these powerful tools, businesses can transform raw data into actionable intelligence, making smarter decisions about everything from product assortment and pricing to supplier negotiations and logistics routes. This comprehensive approach positions ERP not just as a software tool, but as a strategic asset for achieving operational excellence and sustained growth.
Real-Time Data for Retail: Unlocking Supply Chain Transparency with ERP
One of the most profound benefits an ERP system brings to the retail sector is its capacity to deliver real-time data for retail. In an environment where market trends can shift overnight and customer expectations are constantly evolving, having immediate access to accurate information is invaluable. Traditional systems often operate with significant delays, meaning decisions are made based on outdated snapshots rather than the current reality. ERP eradicates this problem by providing a live pulse on every aspect of the supply chain, from stock levels to order status and shipping movements.
Imagine a scenario where a sudden surge in demand for a particular product occurs due to a viral social media trend. With an ERP system, sales data is immediately reflected in inventory levels, triggering alerts if stock is running low. This real-time insight allows procurement teams to quickly place new orders, adjust production schedules, or reallocate stock from other stores or warehouses, minimizing the risk of stockouts and capitalizing on the unexpected demand. Without ERP, such opportunities might be missed, or worse, lead to customer disappointment due to unfulfilled orders.
This continuous flow of current data extends beyond mere inventory management. It encompasses every touchpoint in the supply chain. For instance, tracking shipments becomes far more precise. As goods move through transit, their status is updated directly within the ERP, providing exact locations and estimated arrival times. This transparency allows retailers to proactively communicate with customers about potential delays or confirm successful deliveries, significantly enhancing the customer experience. It also enables logistics managers to identify bottlenecks or issues in transit before they escalate, facilitating quicker problem resolution.
Ultimately, this constant stream of live information fosters a culture of informed decision-making across the organization. Merchandisers can adjust product assortments based on current sales performance, marketing teams can tailor promotions to available inventory, and customer service representatives can provide accurate information regarding order statuses. By eliminating information lags and providing a singular, updated version of the truth, ERP fundamentally transforms how retailers operate, paving the way for true supply chain transparency and greater responsiveness to market dynamics and customer needs.
From Source to Shelf: Achieving End-to-End Control with ERP for Retail Supply Chain Visibility
The ultimate aspiration for any retail business is to have complete command over its entire operational flow, from the initial sourcing of raw materials to the final sale and even post-purchase service. This ideal state is precisely what we mean by achieving end-to-end control, and it’s where ERP truly shines for retail supply chain visibility. An integrated ERP system breaks down the traditional silos between departments, creating a seamless flow of information that connects every stage of the product lifecycle. This comprehensive oversight empowers retailers to manage complexities, mitigate risks, and optimize performance across the board.
Consider the journey of a single product. Before an ERP, information about its components might reside with the procurement team, production details with manufacturing, inventory counts in a separate warehouse system, and sales data in yet another platform. This disjointed approach makes it impossible to trace the product’s full lineage or understand its true cost and profitability. With an ERP, all this data is unified. From vendor selection and purchase order creation to quality control, stock movement, sales transactions, and even return processing, every step is logged and accessible within a single system.
This holistic view allows retailers to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) at every stage. They can track supplier performance, analyze production lead times, evaluate warehouse efficiency, and assess sales velocity—all from a centralized dashboard. If a bottleneck arises in production, for example, the impact on inventory and projected sales can be immediately calculated, allowing management to make quick, informed decisions. This proactive capability is critical for maintaining consistent stock levels, meeting customer demand, and avoiding costly disruptions.
Furthermore, achieving end-to-end control through ERP extends to demand sensing and fulfillment. By integrating historical sales data with current market trends and external factors, an ERP can enhance demand forecasting in retail, allowing retailers to predict future needs with greater accuracy. This precision ensures that the right products are available at the right place and time, minimizing both overstocking and stockouts. The seamless transition from forecast to procurement, production, inventory allocation, and customer order fulfillment is the hallmark of a truly optimized and visible retail supply chain, powered by a robust ERP system.
Strategic Inventory Management for Retail: Preventing Stockouts and Overstocking
One of the most significant challenges in retail is striking the delicate balance in inventory management. Too much stock ties up capital and incurs carrying costs, while too little leads to lost sales and dissatisfied customers. Strategic inventory management for retail is crucial, and an ERP system is the most powerful tool for achieving this equilibrium. By providing real-time, accurate data on stock levels across all locations—stores, warehouses, and in-transit—ERP enables retailers to make highly informed decisions about purchasing, allocation, and replenishment.
An ERP system integrates sales data, purchase orders, production schedules, and return information into a single, comprehensive view of inventory. This means that as soon as a product is sold in a store or online, its stock level is immediately updated across the entire network. This real-time accuracy prevents common issues like selling an item that’s actually out of stock or failing to restock a popular item due to outdated information. Furthermore, it allows for sophisticated inventory strategies such as cross-docking, drop shipping, and omni-channel fulfillment, all orchestrated through a centralized platform.
Beyond simply tracking quantities, ERP systems offer advanced features like demand forecasting, as mentioned earlier. By analyzing historical sales data, seasonality, promotional impacts, and even external market factors, the system can generate highly accurate predictions of future demand. This predictive capability is invaluable for optimizing stock levels, enabling retailers to order just enough to meet anticipated needs without over-committing resources. It minimizes the risk of obsolescence for fashion-forward items and ensures consistent availability for everyday essentials.
Moreover, an ERP system can help segment inventory, categorizing products based on their sales velocity, profitability, and strategic importance. This allows for differentiated inventory strategies—for example, higher safety stock levels for fast-moving items, or just-in-time ordering for slow movers. By automating replenishment triggers based on predefined thresholds and vendor lead times, ERP transforms inventory management from a reactive chore into a proactive, data-driven discipline. This level of granular control is essential not only for operational efficiency but also for significantly improving cash flow and profitability within the retail business.
Optimizing Procurement and Supplier Relations with ERP
The foundation of a healthy supply chain lies in efficient procurement and strong supplier relationships. An ERP system acts as a powerful enabler for optimizing procurement processes in retail, transforming what can often be a cumbersome and fragmented function into a streamlined, strategic operation. By centralizing all purchasing activities, from vendor selection to invoice processing, ERP provides unparalleled visibility and control over the entire purchasing cycle.
With an ERP, retailers can manage their entire vendor database, including contracts, pricing agreements, performance history, and communication logs, all in one place. This centralization makes it easier to compare supplier offerings, negotiate better terms, and ensure compliance with purchasing policies. When a purchase requisition is created, the system can automatically route it for approval, ensuring that all necessary checks and balances are met before an order is placed. This automation drastically reduces manual effort, speeds up the procurement cycle, and minimizes errors.
The integration of procurement with inventory management within the ERP is particularly impactful. As inventory levels drop or demand forecasts indicate a need for more stock, the system can automatically generate purchase orders, sending them directly to pre-approved suppliers. This proactive approach ensures timely replenishment, preventing stockouts and maintaining consistent product availability. Furthermore, the system can track the status of these orders in real-time, providing updates on shipment progress and expected delivery dates, which feeds directly into the retail supply chain visibility objective.
Beyond the transactional aspects, ERP systems also facilitate better supplier relationship management. By maintaining a comprehensive record of supplier performance—including delivery times, quality ratings, and adherence to terms—retailers can identify their most reliable partners and collaborate more effectively. This data-driven approach allows for strategic sourcing, fostering stronger, mutually beneficial relationships that contribute to a more resilient and efficient supply chain. Ultimately, by streamlining procurement, ERP helps retailers reduce costs, improve lead times, and enhance the overall quality of their inventory.
Streamlining Order Management and Fulfillment: Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
In the age of omnichannel retail, customers expect a seamless experience, whether they are shopping online, in-store, or via mobile. Streamlining order management and fulfillment is paramount to meeting these elevated customer expectations and directly contributes to higher customer satisfaction in retail. An ERP system serves as the central orchestrator for all order-related processes, ensuring that every customer interaction, from initial purchase to final delivery, is handled with precision and efficiency.
When an order is placed, regardless of the channel, the ERP system instantly captures and processes it. This immediate integration allows for real-time inventory checks, payment processing, and order confirmation, providing customers with instant feedback. For retailers, it means eliminating delays and reducing the chances of overselling items that are no longer available. The system can then intelligently route the order to the most appropriate fulfillment location—be it a distribution center, a specific store, or even directly from a supplier via dropshipping—based on factors like proximity, stock availability, and shipping costs.
This capability is particularly vital for omnichannel strategies. An ERP can support “buy online, pick up in store” (BOPIS), “ship from store,” and other flexible fulfillment options, offering customers convenience and speed. The system tracks the order’s journey from fulfillment initiation, through packing and shipping, right up to delivery. This comprehensive visibility allows customer service teams to provide accurate updates and proactively address any potential issues, further solidifying customer trust and loyalty.
Moreover, an ERP system often integrates with third-party logistics (3PL) providers and shipping carriers, automating the creation of shipping labels, tracking numbers, and delivery notifications. This level of automation not only speeds up the fulfillment process but also significantly reduces manual errors and operational costs. By ensuring that orders are processed quickly, accurately, and with full transparency, ERP empowers retailers to exceed customer expectations, turning every purchase into a positive and memorable experience, thereby directly boosting overall customer satisfaction.
Maximizing Warehouse Efficiency with Integrated ERP Solutions
The warehouse is the pulsating heart of any retail supply chain, and its efficiency directly impacts speed, accuracy, and cost. Leveraging an integrated ERP solution is crucial for maximizing warehouse efficiency, transforming a complex operational hub into a highly optimized and responsive entity. An ERP system, often coupled with a dedicated Warehouse Management System (WMS) module, provides the tools necessary to manage inventory movement, storage, and order picking with unparalleled precision.
Through an ERP’s WMS capabilities, retailers gain full visibility into the exact location of every item within the warehouse, optimizing storage allocation and minimizing retrieval times. Items can be dynamically assigned to specific bins or zones based on their size, weight, sales velocity, or special handling requirements. This intelligent organization reduces search times for pickers and streamlines the entire picking process, whether it’s for individual e-commerce orders or large bulk shipments to retail stores.
The system also automates critical warehouse processes. For instance, when new inventory arrives, the ERP guides receiving teams through verification, quality checks, and putaway, ensuring items are accurately logged and placed in their designated locations. For outbound orders, it optimizes picking routes, often using technologies like barcode scanning or RFID to ensure pick accuracy and minimize errors. This level of automation significantly cuts down on manual labor, reduces the likelihood of shipping incorrect items, and accelerates throughput.
Beyond basic management, an ERP with advanced WMS functionality can also support labor management, helping warehouse managers optimize staffing levels based on workload forecasts. It can track picker performance, identify areas for training, and ensure compliance with safety protocols. By integrating with other ERP modules like inventory and procurement, the warehouse becomes an integral, visible part of the end-to-end supply chain. This holistic approach to warehouse management ensures that goods flow seamlessly, contributing directly to faster fulfillment, lower operational costs, and ultimately, enhanced ERP for retail supply chain visibility.
Logistics Optimization and Transportation Management within ERP
Effective logistics and transportation are the arteries of the retail supply chain, ensuring products move efficiently from origin to destination. An ERP system, particularly one with strong logistics and transportation management capabilities, is instrumental for logistics optimization, allowing retailers to plan, execute, and monitor the movement of goods with greater precision and cost-effectiveness. This integration provides a bird’s-eye view of all shipping activities, a critical component for achieving end-to-end control over the entire supply chain.
Within the ERP, retailers can manage a database of carriers, negotiate freight rates, and select the most optimal shipping methods based on cost, speed, and reliability. The system can consolidate orders, plan multi-stop routes, and even optimize truck loading to maximize capacity and reduce fuel consumption. This intelligent planning goes beyond simple order dispatch; it involves complex algorithms that consider various factors like geographic locations, delivery windows, and vehicle availability to create the most efficient logistics plan.
Real-time tracking is another cornerstone of ERP-enabled logistics optimization. As shipments depart, the system updates their status, allowing managers to monitor progress and anticipate potential delays. This immediate feedback loop is invaluable for proactive problem-solving. If a shipment is delayed due to weather or an unforeseen event, the ERP can immediately trigger alerts, allowing retailers to inform affected customers, re-route other shipments if necessary, or make alternative arrangements. This level of transparency is vital for maintaining customer trust and operational agility.
Furthermore, an ERP facilitates comprehensive freight auditing and payment processing, ensuring that carriers are billed accurately according to negotiated rates. It also provides valuable data for analyzing transportation costs, identifying areas for improvement, and evaluating carrier performance over time. By integrating logistics and transportation management into the broader ERP framework, retailers gain unprecedented insight and control over their entire distribution network. This ensures products arrive on time, at the lowest possible cost, and with full visibility, directly enhancing ERP for retail supply chain visibility and operational excellence.
Enhancing Demand Forecasting in Retail for Smarter Planning
Accurate demand forecasting in retail is the cornerstone of efficient supply chain management. Without a clear understanding of what customers will want and when, retailers face a constant battle against stockouts, overstocking, and missed sales opportunities. An ERP system significantly enhances forecasting capabilities by integrating vast amounts of data and applying advanced analytical tools, transforming guesswork into data-driven prediction.
Traditional forecasting often relies on historical sales data alone, which can be insufficient in today’s dynamic market. An ERP system goes much further by consolidating internal data—like past sales, promotional impacts, pricing changes, and seasonal trends—with external factors such as economic indicators, weather patterns, social media trends, and competitive activities. By bringing all this diverse information into a single platform, the ERP can build a more comprehensive and accurate picture of future demand.
Modern ERPs often incorporate machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to analyze these complex datasets. These intelligent systems can identify subtle patterns and correlations that human analysts might miss, refining forecasts with increasing precision over time. For example, an ERP might predict a surge in umbrella sales based on a combination of historical weather data, current forecasts, and recent purchasing trends in similar regions, allowing the retailer to proactively adjust inventory.
The benefits of improved demand forecasting ripple throughout the entire supply chain. Procurement teams can place orders with greater confidence, reducing the risk of either over-ordering perishable goods or facing stockouts of popular items. Production schedules can be optimized, warehouse space allocated more effectively, and marketing campaigns aligned with projected product availability. This foresight, enabled by ERP, leads to reduced waste, lower carrying costs, and significantly improved customer satisfaction by ensuring products are available when and where they are needed most. It is a critical element in achieving end-to-end control and maximizing ERP for retail supply chain visibility.
The Role of CRM Integration: Customer-Centric Supply Chain Management
While often seen as a separate function, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is intrinsically linked to the supply chain, especially in retail. Integrating CRM functionalities within an ERP system, or ensuring seamless data exchange between standalone CRM and ERP, creates a truly customer-centric supply chain management approach. This integration ensures that customer insights drive supply chain decisions, ultimately leading to a more responsive and satisfying retail experience.
When CRM data is integrated with ERP, information about customer preferences, purchase history, loyalty program status, and feedback becomes directly accessible to supply chain managers. This allows retailers to personalize their offerings and tailor their supply chain strategies. For example, if CRM data indicates a growing demand for eco-friendly products among a significant customer segment, the procurement team can prioritize sourcing from sustainable suppliers, and the inventory team can ensure adequate stock levels for these specific items.
Beyond strategic planning, CRM integration enhances operational aspects of the supply chain. Customer service representatives, empowered by unified data from both CRM and ERP, can provide highly accurate and personalized assistance. They can instantly see a customer’s order history, real-time order status, shipping details, and even previous interactions. This comprehensive view enables them to quickly resolve issues, manage expectations regarding delivery, and offer proactive solutions, significantly boosting customer loyalty.
Furthermore, post-purchase processes like returns and exchanges become much smoother. With integrated CRM and ERP, the system instantly recognizes the customer, retrieves their purchase details, and guides the return process seamlessly, from initiation to refund or exchange. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and speeds up resolution, turning a potentially negative experience into an opportunity to reinforce customer trust. By putting the customer at the heart of the supply chain, ERP with CRM integration truly elevates ERP for retail supply chain visibility from a purely logistical perspective to a customer-driven strategic advantage.
Financial Management Integration: Tying the Supply Chain Together
The ultimate measure of a supply chain’s success is its impact on the bottom line. This is where the robust financial management integration capabilities of an ERP system become indispensable, effectively tying the supply chain together from a fiscal perspective. By unifying financial data with operational data, ERP provides retailers with a complete and accurate financial picture of their supply chain, enabling better budgeting, cost control, and profitability analysis.
Every transaction that occurs within the supply chain—from a purchase order to a sales transaction, a shipment fee, or a return processing cost—has a financial implication. An ERP system automatically captures and records these financial events, feeding them directly into the general ledger, accounts payable, and accounts receivable modules. This automation eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and ensures that financial records are always up-to-date and reconciled with operational activities.
This integration allows retailers to accurately track the true cost of goods sold (COGS), factoring in not just the purchase price but also associated logistics, warehousing, and handling costs. By having this granular financial visibility, businesses can analyze the profitability of individual products, suppliers, or even specific sales channels. This insight is crucial for making informed decisions about pricing strategies, product assortment, and vendor negotiations.
Moreover, ERP’s financial modules support comprehensive budgeting and forecasting for supply chain operations. Managers can set budgets for inventory holding costs, transportation expenses, and warehouse operations, and then track actual spending against these budgets in real-time. This allows for proactive identification of cost overruns and timely adjustments to spending. By providing a holistic view of both operational performance and its financial consequences, ERP empowers retailers to optimize their supply chain not just for efficiency, but for maximum profitability, demonstrating how deeply achieving end-to-end control is tied to sound financial management.
Leveraging Data Analytics and Reporting for Strategic Decision-Making
Beyond simply collecting data, the true power of an ERP system for retail supply chain visibility lies in its ability to transform raw information into actionable insights through robust data analytics and reporting. Modern ERP solutions come equipped with sophisticated analytical tools, dashboards, and reporting functionalities that empower retailers to move beyond reactive management and engage in proactive, strategic decision-making. This capability is fundamental to continuously optimizing the supply chain and maintaining a competitive edge.
An ERP’s analytical engine can process vast quantities of data from all integrated modules—sales, inventory, procurement, logistics, finance, and CRM. It can identify trends, highlight anomalies, and generate predictive models that would be impossible to discern through manual analysis. For example, a dashboard might show real-time stock levels alongside sales velocity and projected demand, immediately flagging products that are at risk of stockouts or overstock. It can also analyze supplier performance over time, identifying which vendors consistently deliver on time and within budget, guiding future procurement decisions.
Customizable reports allow retailers to slice and dice data in numerous ways, answering specific business questions. Want to know the profitability of a specific product category across different regions? Or the impact of a recent promotion on inventory turnover? The ERP can generate these reports on demand. These insights are not just for high-level executives; they empower managers at every level, from warehouse supervisors to store managers, to make better operational decisions based on concrete data rather than intuition.
Furthermore, many ERPs offer advanced business intelligence (BI) capabilities, enabling users to create interactive visualizations and drill down into data points. This allows for a deeper understanding of underlying causes and effects within the supply chain. By continuously monitoring KPIs, identifying patterns, and predicting future scenarios, retailers can proactively address potential issues, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and refine their strategies. This data-driven approach is a game-changer for achieving end-to-end control, ensuring that every decision is backed by solid evidence and contributing to sustained business success.
Seamless Integration with External Systems: Extending Supply Chain Reach
The retail supply chain doesn’t operate in isolation; it constantly interacts with a multitude of external partners and platforms. For achieving end-to-end control and true ERP for retail supply chain visibility, seamless integration with external systems is paramount. A modern ERP system is designed to connect effortlessly with various third-party applications, expanding its reach and ensuring a continuous flow of data across the entire ecosystem.
One of the most critical external integrations is with e-commerce platforms. For retailers with an online presence, the ERP must be able to synchronize inventory levels, process online orders, update product catalogs, and manage customer data in real-time with platforms like Shopify, Magento, or Salesforce Commerce Cloud. This prevents overselling, ensures accurate product information online, and streamlines the order fulfillment process from web checkout to doorstep delivery. Without this tight integration, the omnichannel experience for customers would be fragmented and unreliable.
Another vital area is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). Many retailers rely on EDI for automated communication with suppliers, manufacturers, 3PLs, and even major retail partners. An ERP that supports EDI allows for the automatic exchange of purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and inventory reports, significantly reducing manual data entry, speeding up transaction times, and minimizing errors. This is particularly crucial for businesses dealing with high volumes of transactions or working with partners who mandate EDI compliance.
Beyond e-commerce and EDI, ERP systems can integrate with other external solutions such as payment gateways, marketing automation platforms, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and even IoT devices in warehouses or vehicles. For instance, connecting to an IoT sensor on a delivery truck could provide real-time temperature monitoring for perishable goods, feeding critical data directly into the ERP. These integrations collectively create a truly interconnected supply chain, extending visibility and control far beyond the traditional boundaries of the retail organization, ensuring that every touchpoint is aligned and optimized.
Digital Transformation in Retail: Embracing Modern ERP Implementation
Embarking on an ERP journey is more than just installing new software; it’s a fundamental shift in how a retail business operates, representing a significant stride towards digital transformation in retail. Embracing modern ERP implementation is about reimagining processes, leveraging technology to its fullest, and creating a more agile, data-driven organization. This transformation is essential for retailers looking to maintain relevance and competitiveness in an increasingly digital marketplace.
A successful ERP implementation begins with a thorough understanding of current business processes and identifying areas for improvement. This often involves a comprehensive review of existing workflows, pinpointing inefficiencies, and aligning them with the best practices embedded within the ERP system. It’s an opportunity to standardize operations, eliminate redundant tasks, and introduce automation, thereby enhancing overall operational efficiency. The goal is not just to automate old processes but to innovate and optimize them using the capabilities of the new system.
Change management is a critical component of this digital transformation. Implementing an ERP impacts every department and every employee, requiring significant adjustments to daily routines. Effective communication, comprehensive training programs, and strong leadership buy-in are crucial to ensure user adoption and minimize resistance to change. Retailers must invest in preparing their teams for the new way of working, highlighting the benefits and providing the necessary support to navigate the transition smoothly.
Ultimately, embracing modern ERP implementation is an investment in the future resilience and growth of the retail business. It provides the technological foundation for scalability, allowing retailers to expand into new markets, introduce new product lines, or adapt to changing business models with greater ease. By establishing a unified, intelligent platform for all core operations, ERP accelerates digital transformation, enabling retailers to not only achieving end-to-end control but also to continuously innovate and thrive in the ever-evolving retail landscape.
Overcoming Common Challenges in ERP Adoption: Navigating the Implementation Journey
While the benefits of an ERP system for retail supply chain visibility are clear, the implementation journey can present its own set of hurdles. Addressing common challenges in ERP adoption proactively is crucial for a smooth and successful transition. Understanding these potential pitfalls and having a strategy to navigate them can significantly mitigate risks and ensure that the investment yields its intended returns.
One of the most significant challenges often revolves around data migration. Retailers typically have vast amounts of historical data residing in various legacy systems, spreadsheets, or even physical records. Extracting, cleaning, transforming, and loading this data into the new ERP system can be a complex and time-consuming process. Inaccurate or incomplete data migration can lead to significant problems post-implementation, impacting everything from inventory counts to financial reporting. A meticulous data strategy, thorough validation, and dedicated resources are essential to overcome this.
Another common hurdle is user resistance and lack of adoption. Employees, accustomed to their old ways of working, may find the new system complex or disruptive to their routines. Without proper training, clear communication about the benefits, and ongoing support, users may struggle to fully embrace the ERP, leading to underutilization and a failure to realize the system’s full potential. Strong change management, executive sponsorship, and a focus on user-friendly interfaces are key to fostering enthusiastic adoption.
Finally, managing the scope and budget of an ERP project can be challenging. “Scope creep,” where new features or customizations are continually added during the implementation phase, can lead to delays and cost overruns. It’s vital to have a clear project scope defined upfront, with strict change control procedures in place. Choosing the right implementation partner and maintaining realistic expectations about timelines and resource requirements are also critical factors in ensuring the project stays on track and within budget, ultimately making the journey to achieving end-to-end control a rewarding one.
The Future of Retail Supply Chains: AI, ML, and IoT in ERP
The evolution of ERP systems for retail supply chains is far from over. The integration of cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) is paving the way for unprecedented levels of automation, intelligence, and visibility. These advancements promise to further revolutionize ERP for retail supply chain visibility, pushing beyond current capabilities and ushering in an era of hyper-optimized and predictive operations.
AI and ML are already beginning to transform key areas of the supply chain. In demand forecasting, ML algorithms can analyze even more complex datasets and learn from past outcomes, continuously improving prediction accuracy. This allows for dynamic adjustments to inventory levels in real-time based on subtle market shifts or unforeseen events. Beyond forecasting, AI can optimize warehouse layouts, predict equipment maintenance needs, and even automate pricing strategies based on competitor analysis and current stock levels, leading to proactive rather than reactive management.
The Internet of Things (IoT) adds a physical layer of intelligence to the supply chain. Imagine sensors on individual products, shelves, or delivery vehicles that continuously feed data back into the ERP system. IoT devices can track the precise location of inventory, monitor environmental conditions (like temperature and humidity for perishable goods), and even identify bottlenecks on a factory floor or within a distribution center. This granular, real-time data from the physical world empowers the ERP to create a digital twin of the supply chain, providing unprecedented transparency.
When combined, AI, ML, and IoT create a truly intelligent and self-optimizing retail supply chain. ERP systems will be able to not only collect vast amounts of data but also interpret it, learn from it, and even make autonomous decisions. For instance, if an IoT sensor detects a delay in a critical shipment, an AI-powered ERP could automatically re-route other orders, inform affected customers, and adjust replenishment plans without human intervention. This future vision of an intelligent, autonomous supply chain underscores the ongoing journey towards truly achieving end-to-end control, making the retail supply chain more resilient, efficient, and responsive than ever before.
Measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of ERP for Retailers
Investing in an ERP system is a significant undertaking, and naturally, retailers need to understand the tangible benefits and financial returns. Measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of ERP for retailers involves evaluating both the direct cost savings and the indirect strategic advantages gained from enhanced ERP for retail supply chain visibility. A clear understanding of ROI helps justify the initial investment and demonstrates the long-term value generated by the system.
Direct cost savings can be identified in several areas. Automation of manual processes across procurement, inventory management, and order fulfillment reduces labor costs and minimizes errors that lead to rework or costly mistakes. Optimized inventory levels, achieved through better forecasting and management, decrease carrying costs (warehousing, insurance, obsolescence) and reduce capital tied up in excess stock. Improved logistics planning leads to lower transportation expenses and more efficient use of resources. Furthermore, enhanced data accuracy helps in identifying and eliminating fraudulent activities and ensures compliance, reducing potential fines or losses.
Beyond direct cost reductions, ERP delivers substantial indirect benefits that significantly contribute to ROI. Increased supply chain visibility leads to fewer stockouts, which translates directly into increased sales and improved customer satisfaction. Faster order fulfillment and more reliable delivery times enhance the customer experience, fostering loyalty and driving repeat business. Better data analytics enable more strategic decision-making, leading to improved product assortment, more effective marketing campaigns, and ultimately, higher profitability margins.
Calculating ROI typically involves comparing the total costs of ERP implementation (software, hardware, training, consulting, ongoing maintenance) against the quantifiable benefits over a specific period. Many retailers find that the benefits accrue rapidly, with significant improvements in operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and financial performance becoming evident within months or a few years. Ultimately, an ERP system empowers retailers to not just save money, but to grow their business more strategically and profitably, solidifying its role in achieving end-to-end control and delivering a strong return on investment.
Choosing the Right ERP: Factors for a Successful Retail Implementation
The decision to implement an ERP system is monumental, and choosing the right ERP is a critical first step towards a successful retail implementation. Given the wide array of ERP solutions available, retailers must carefully consider several key factors to select a system that aligns perfectly with their specific business needs, strategic goals, and long-term vision for achieving end-to-end control and superior ERP for retail supply chain visibility.
Firstly, industry-specific functionality is paramount. While generic ERPs exist, a solution tailored specifically for retail will offer out-of-the-box features that address the unique complexities of the retail supply chain—such as omnichannel order management, robust inventory management for diverse product assortments, promotional planning, and integration with POS systems. These specialized functionalities often require less customization, leading to a smoother implementation and quicker time to value.
Scalability and flexibility are also crucial considerations. The chosen ERP should be able to grow with the business, accommodating future expansion into new markets, new product lines, or increased transaction volumes without requiring a complete overhaul. It should also be flexible enough to adapt to evolving business processes and integrate with emerging technologies. Cloud-based ERP solutions often offer greater scalability and flexibility, along with reduced infrastructure maintenance costs, making them an attractive option for modern retailers.
Finally, the vendor’s reputation, support, and implementation expertise cannot be overstated. A reputable vendor with a proven track record in retail ERP implementations can provide invaluable guidance throughout the project. Their support capabilities, training programs, and ongoing maintenance services are critical for long-term success. Engaging with a vendor and implementation partner who understands the unique challenges and opportunities of the retail sector is key to ensuring that the chosen ERP system truly becomes the strategic asset needed to revolutionize the supply chain and deliver comprehensive end-to-end control.
Conclusion: The Imperative of ERP for a Visible and Controlled Retail Supply Chain
In an era defined by rapid change, intense competition, and increasingly demanding customers, the quest for superior operational control and comprehensive visibility has become an imperative for every retailer. Our extensive exploration has unequivocally demonstrated that a robust ERP system is not just a tool, but the foundational pillar for achieving end-to-end control across the intricate web of the retail supply chain. It transforms fragmentation into integration, uncertainty into clarity, and reactivity into strategic foresight.
From optimizing procurement and inventory management to streamlining order fulfillment and enhancing customer satisfaction, ERP acts as the central nervous system that connects every function, ensuring that data flows freely and decisions are made on a foundation of real-time accuracy. It empowers retailers to overcome challenges like stockouts and overstocking, leverage powerful data analytics for strategic growth, and embrace the future of retail with technologies like AI, ML, and IoT. The journey of ERP for retail supply chain visibility is one of continuous improvement, where every integration and optimization contributes to a more resilient, efficient, and profitable business.
The shift to an ERP-driven supply chain isn’t merely an operational upgrade; it’s a strategic transformation that positions retailers for sustained success in a dynamic global market. By embracing this powerful technology, businesses can unlock unparalleled transparency, drive operational excellence, and ultimately deliver superior value to their customers. The future of retail belongs to those who can see clearly and act decisively—a future made possible by the comprehensive vision and control that only an integrated ERP system can provide. Make the move towards full supply chain visibility and control, and watch your retail business thrive.