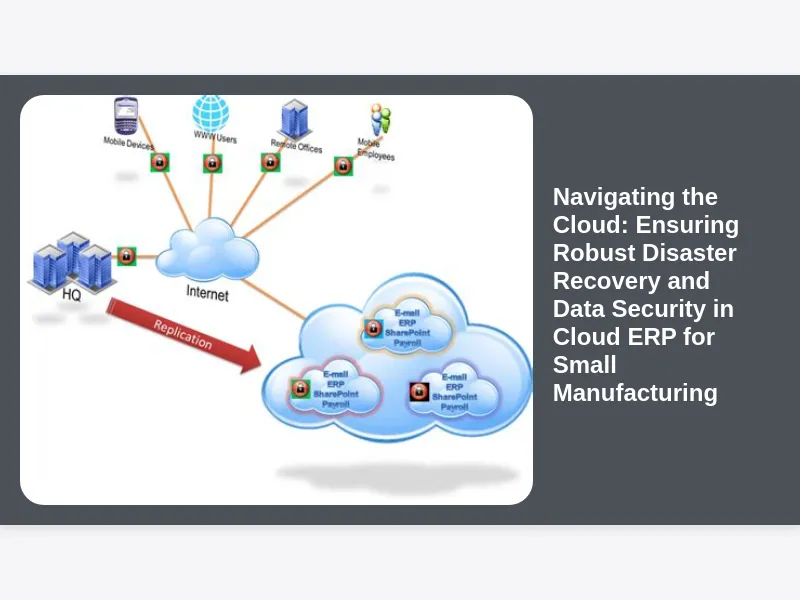
The landscape of modern manufacturing is rapidly evolving, with small manufacturing businesses increasingly turning to cloud-based Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. While the allure of cloud ERP — offering scalability, flexibility, and reduced infrastructure costs — is undeniable, it also introduces a critical set of considerations: how do we ensure the resilience of our operations against unforeseen disruptions and protect our invaluable data in this new environment? For small manufacturers, the shift to the cloud is not just about adopting new technology; it’s about strategically ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing to safeguard their future.
Moving your core business processes and sensitive data to the cloud inherently shifts some aspects of responsibility, but it doesn’t diminish the manufacturer’s ultimate accountability for their data’s integrity and availability. This article delves deep into the essential strategies, best practices, and proactive measures that small manufacturing companies must embrace to build a robust framework for both disaster recovery and comprehensive data security within their cloud ERP ecosystem. It’s about empowering these businesses not just to survive, but to thrive, even when faced with the unexpected, by meticulously planning for continuity and impregnable security from the ground up.
The Digital Imperative: Why Cloud ERP is Essential for Modern Small Manufacturers
For many small manufacturing businesses, traditional on-premise ERP systems represented a significant financial and operational burden. The cost of purchasing hardware, licensing software, and maintaining dedicated IT staff often put sophisticated enterprise solutions out of reach. Cloud ERP, however, democratizes access to powerful tools, allowing smaller players to leverage capabilities once reserved for large corporations, from enhanced production planning to streamlined inventory management and real-time financial reporting. This accessibility is transforming how these businesses operate, fostering greater agility and responsiveness in a dynamic market.
The advantages extend beyond mere cost savings. Cloud ERP solutions offer unparalleled scalability, meaning a manufacturer can easily adjust their resource allocation based on seasonal demands, new product launches, or market fluctuations, without significant capital expenditure. They also promote greater collaboration across departments, as all employees access a single, unified source of truth, regardless of their physical location. This seamless integration of business processes is a powerful catalyst for efficiency and innovation, positioning small manufacturers to compete more effectively in global supply chains. However, this transition also brings forth new complexities, making the question of ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing more pertinent than ever before.
Understanding Cloud ERP’s Value Proposition Beyond Basic Cost Savings
While the financial benefits of cloud ERP, such as converting capital expenditure into operational expenditure and reducing IT overheads, are often the primary drivers for adoption, its true value for small manufacturers lies in its strategic advantages. Cloud solutions inherently offer a level of agility that on-premise systems struggle to match. Businesses can quickly deploy new modules, integrate with other cloud-based applications, and adapt to changing market conditions with far greater speed. This responsiveness is crucial in an era where supply chains are increasingly volatile and customer demands are rapidly shifting.
Furthermore, cloud ERP typically comes with automatic updates and maintenance handled by the provider, ensuring that the manufacturing business always has access to the latest features and security patches without diverting internal resources. This continuous improvement model means that as new technologies emerge or compliance standards evolve, the ERP system can adapt without requiring expensive, time-consuming upgrades. This ability to stay current and leverage cutting-edge capabilities truly unlocks the potential for small manufacturers to innovate and optimize their operations, provided they simultaneously focus on ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing as a foundational element of their strategy.
The Unique Cybersecurity Landscape for Small Manufacturing SMEs
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), particularly in the manufacturing sector, often face a disproportionate amount of cybersecurity risk. They are frequently perceived as “soft targets” by cybercriminals because they may have fewer dedicated IT security resources and less sophisticated defenses compared to larger corporations. However, they hold valuable intellectual property, customer data, and supply chain insights, making them attractive targets for ransomware attacks, industrial espionage, and business email compromise (BEC) schemes. The impact of a successful cyberattack on a small manufacturer can be catastrophic, leading to operational downtime, data loss, reputational damage, and significant financial penalties.
Manufacturing operations, with their interconnected machinery and reliance on operational technology (OT) alongside IT, present a complex attack surface. A breach in one area, such as a cloud ERP system managing production schedules, could ripple through the entire operation, impacting smart factory components or even physical machinery. This intricate web of dependencies underscores why a proactive and robust approach to security is not merely a best practice but an absolute necessity. Businesses need to understand these specific vulnerabilities when strategizing for ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Defining Disaster Recovery in a Cloud ERP Context: Beyond Simple Backups
Disaster recovery (DR) in the context of cloud ERP for small manufacturing extends far beyond simply backing up data. It encompasses a comprehensive strategy designed to restore business-critical functions and data quickly and efficiently after any disruptive event, whether it’s a natural disaster, a cyberattack, a major system failure, or human error. For a manufacturing operation, this means not just getting the ERP system back online, but ensuring that production schedules can resume, inventory levels are accurate, and financial transactions are recovered without significant loss. The goal is to minimize downtime and the financial and reputational damage associated with it.
Key to an effective cloud ERP disaster recovery plan are well-defined Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO). RTO dictates the maximum acceptable delay before critical business functions are restored, essentially how long the business can afford to be down. RPO, on the other hand, defines the maximum amount of data that can be lost from the point of failure until recovery. For a manufacturer, even a few hours of downtime can mean thousands of dollars in lost production, missed deadlines, and contractual penalties. Therefore, meticulously planning and regularly testing these objectives is paramount when ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Pivotal Pillars of Data Security in Cloud ERP Environments: A Shared Responsibility
Data security in a cloud ERP environment is built upon several fundamental principles, all working in concert to protect sensitive manufacturing data. Encryption, both in transit and at rest, is a non-negotiable baseline, scrambling data into unreadable code to prevent unauthorized access even if breached. Robust access controls ensure that only authorized personnel can access specific data and functionalities within the ERP system, adhering to the principle of least privilege. Furthermore, network security measures, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems, form the perimeter defense against external threats targeting the cloud infrastructure.
It’s crucial for small manufacturers to understand the shared responsibility model inherent in cloud computing. While the cloud provider is responsible for the security of the cloud (e.g., the underlying infrastructure, physical security of data centers), the customer remains responsible for security in the cloud (e.g., configuration of their ERP instance, data classification, access management). This means actively managing user permissions, implementing strong authentication, and configuring security settings within their ERP application. Neglecting this customer-side responsibility can create significant vulnerabilities, underscoring the collaborative effort required for ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Evaluating Cloud ERP Providers: A Security-First Approach to Vendor Selection
The choice of a cloud ERP vendor is perhaps the single most critical decision a small manufacturer will make regarding their data security and disaster recovery posture. It’s imperative to go beyond feature sets and pricing, thoroughly scrutinizing the vendor’s security practices, certifications, and track record. Ask pointed questions about their data center security, encryption protocols, incident response capabilities, and how they handle data privacy and compliance. Do they offer multi-factor authentication (MFA)? What are their uptime guarantees and how are they achieved?
Look for vendors that adhere to internationally recognized security standards and certifications, such as ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type 2, or NIST frameworks. These certifications indicate that the provider has undergone rigorous audits of their security controls and processes. Review their Service Level Agreements (SLAs) regarding uptime, data recovery times, and security incident notifications. A reputable vendor will be transparent about their security measures and willing to answer all your questions, providing confidence that they are a strong partner in ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Implementing Robust Backup and Restoration Strategies for Cloud ERP
Even in the cloud, having a meticulously planned and frequently tested backup and restoration strategy is fundamental to disaster recovery. Cloud ERP providers typically offer their own backup services, often with geographical redundancy to protect against localized disasters. However, small manufacturers should still understand the specifics of these backups: how frequently are they performed, for how long are they retained, and what is the process for restoring data? It’s wise to consider additional layers of backup, such as exporting critical data periodically to an independent, secure storage location, thereby maintaining a separate copy under your direct control.
The true test of any backup strategy lies in its restoration capabilities. Regular, simulated disaster recovery drills are essential to validate the integrity of backups and the efficiency of the restoration process. These drills should involve key personnel and test the RTO and RPO objectives established for the business. This isn’t a one-time exercise; as your manufacturing processes evolve and your data grows, your backup and restoration strategy must be reviewed and updated to remain effective. Proactive testing is the bedrock of ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Access Control and Identity Management: Fortifying Your Cloud ERP Perimeter
Precise access control and robust identity management are indispensable for safeguarding your cloud ERP system from both external threats and internal misuse. Implementing the principle of “least privilege” ensures that users only have access to the data and functionalities absolutely necessary for their job roles. This means granular permissions for different departments and individual employees, rather than broad, all-encompassing access. Role-based access control (RBAC) is an effective way to manage these permissions systematically, assigning predefined roles with specific privileges to users.
Beyond permissions, strong authentication mechanisms are paramount. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be mandatory for all users accessing the cloud ERP, adding an extra layer of security beyond a simple password. Regular audits of user accounts and access logs are also critical to detect any unauthorized activity or unusual patterns, helping to identify potential breaches early. Effectively managing who can access what, and verifying their identity repeatedly, significantly strengthens the overall security posture and is a core component of ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Threat Detection, Monitoring, and Incident Response Planning in the Cloud
Proactive threat detection and continuous monitoring are vital for identifying security incidents before they escalate into full-blown breaches. Modern cloud ERP solutions often include built-in logging and monitoring capabilities, but small manufacturers should also consider leveraging Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools, either standalone or as a service, to aggregate and analyze security logs from their ERP and other connected systems. This centralized visibility can help detect anomalies, suspicious activities, and potential attack patterns in real time.
Equally important is a well-defined and regularly practiced incident response plan. This plan outlines the steps to be taken immediately following a security incident, including identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. For a small manufacturer, this means knowing precisely who to contact, what data needs to be isolated, and how to communicate with affected parties. Having a clear, actionable plan minimizes chaos during a crisis and dramatically reduces the potential damage, solidifying the efforts put into ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Navigating Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards for Cloud ERP
Manufacturing, like many industries, is subject to various regulatory compliance requirements, some of which directly impact data handling and security. While regulations like GDPR or HIPAA might seem less directly applicable than in healthcare or finance, they set precedents for data privacy that even manufacturers dealing with customer or employee data must heed. Furthermore, industry-specific standards (e.g., related to quality management like ISO 9001, or cybersecurity frameworks like NIST SP 800-171 for defense contractors) often mandate specific controls for information security, which must be extended to cloud ERP systems.
Small manufacturers need to assess their specific compliance obligations and ensure their chosen cloud ERP solution and its configuration meet these requirements. This involves understanding how the cloud provider handles data residency, privacy, and security controls, and then mapping these against their own compliance checklist. Maintaining comprehensive documentation of security policies, procedures, and audit trails is not just a best practice but often a regulatory necessity. This diligent attention to compliance is a non-negotiable aspect of ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Employee Training: The Human Element of Cloud Security Resilience
Technology and robust systems are only part of the security equation; the human element remains the weakest link if not properly addressed. Employees, from the factory floor to the accounting department, are often the first line of defense against cyber threats like phishing attacks, social engineering, and malware. A single click on a malicious link can compromise an entire cloud ERP system, leading to data breaches or ransomware infections. Therefore, continuous and comprehensive employee training on cybersecurity best practices is absolutely crucial.
Training should cover topics such as recognizing phishing attempts, creating strong and unique passwords, understanding the risks of shadow IT, and knowing how to report suspicious activity. It should also emphasize the importance of data privacy and the company’s security policies. Building a security-conscious culture where every employee understands their role in protecting sensitive information is as vital as any firewall or encryption protocol. Investing in this human firewall is a strategic step in ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Risk Assessment and Continuous Improvement for Cloud ERP Security
Adopting a “set it and forget it” mentality towards cloud ERP security is a recipe for disaster in an ever-evolving threat landscape. Small manufacturers must implement a continuous process of risk assessment to identify new vulnerabilities, evaluate potential threats, and assess the effectiveness of existing security controls. This involves periodic vulnerability scans, penetration testing (where appropriate and with provider permission), and regular reviews of security policies and configurations.
The insights gained from these assessments should feed into a continuous improvement cycle. As new security patches are released, as employees join or leave, or as the business expands, security measures must adapt. Staying informed about the latest cyber threats and industry best practices is also critical. This proactive, iterative approach ensures that the cloud ERP environment remains resilient against emerging risks, making continuous improvement a cornerstone of ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis of Investing in Cloud ERP Disaster Recovery and Security
For small manufacturing businesses, every investment decision undergoes intense scrutiny, and security measures are no exception. While the upfront costs of advanced security tools, employee training, and consulting services might seem significant, it’s crucial to view these not as expenses, but as strategic investments that yield substantial long-term benefits. The cost of preventing a disaster or a data breach is almost always exponentially lower than the cost of recovering from one.
Consider the potential financial implications of a security incident: lost production time, recovery costs, legal fees, regulatory fines, and potential loss of customer trust and market share. Beyond the tangible financial impact, the damage to a small manufacturer’s reputation can be irreparable, affecting future contracts and partnerships. Investing proactively in robust disaster recovery and data security for their cloud ERP not only safeguards their operations and data but also protects their brand, ensures business continuity, and builds trust with stakeholders, ultimately reinforcing their position in the market. This clearly demonstrates the immense value in ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Integrating Supply Chain Security with Your Cloud ERP Strategy
Small manufacturers are often integral links in larger supply chains, making them targets for cyberattacks aimed at disrupting the entire chain or gaining access to data from larger partners. A breach in a small manufacturer’s cloud ERP could expose sensitive information that compromises the security of their customers or suppliers. Therefore, a comprehensive security strategy must extend beyond the internal organization to encompass the entire supply chain. This means carefully vetting third-party vendors and partners who may have access to your cloud ERP or integrate with it.
Manufacturers need to establish clear security requirements for their suppliers and customers, potentially requiring them to adhere to specific cybersecurity standards or sign data protection agreements. Furthermore, understanding the security postures of their own cloud ERP vendor’s sub-processors is also critical. Managing third-party risks effectively becomes a shared responsibility that strengthens the resilience of the entire supply chain. By proactively managing these external dependencies, small manufacturers add another vital layer to ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Future-Proofing Your Manufacturing Operations: AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Security
The landscape of cybersecurity is dynamic, with threats constantly evolving in sophistication and volume. To truly future-proof their manufacturing operations, small businesses need to stay abreast of emerging technologies that can enhance their cloud security posture. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are rapidly becoming indispensable tools in this fight, offering capabilities that go beyond traditional rule-based security systems. AI/ML can analyze vast amounts of data from ERP logs, network traffic, and user behavior in real-time, identifying anomalies and predictive patterns that human analysts might miss.
These advanced analytics can detect sophisticated threats like zero-day attacks, insider threats, and highly evasive malware, often before they cause significant damage. Predictive analytics can even forecast potential vulnerabilities or attack vectors based on historical data and current threat intelligence. While implementing these cutting-edge technologies might seem daunting for a small manufacturer, many cloud ERP providers and third-party security services are beginning to integrate AI/ML-driven security features, making them more accessible. Embracing these innovations is a forward-thinking approach to ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Beyond the Technical: Business Continuity Planning (BCP) for Manufacturers
While disaster recovery specifically focuses on restoring IT systems and data, business continuity planning (BCP) takes a broader, holistic view of keeping the entire manufacturing operation running in the face of any disruption. For a small manufacturer, this means considering not just the cloud ERP system, but also critical machinery, raw material supply, logistics, utilities, and personnel. What happens if the factory loses power? How will production continue if a key supplier goes out of business? How will employees access their workstations if the main office is inaccessible?
A comprehensive BCP identifies all critical business functions, assesses the potential impact of various disruptions on each, and develops strategies to maintain operational capabilities or rapidly restore them. This often involves cross-functional teams, clear communication protocols, and alternative operational procedures. Integrating the cloud ERP disaster recovery plan seamlessly into the overarching BCP ensures that the technological resilience supports the overall business resilience. This holistic perspective is fundamental to ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing from an operational standpoint.
The Role of Automation in Enhancing Disaster Recovery and Data Security
Automation plays an increasingly critical role in strengthening both disaster recovery and data security within cloud ERP environments, particularly for small manufacturers with limited IT staff. Automated backups, for instance, eliminate the risk of human error or forgotten tasks, ensuring that data is consistently saved according to predefined schedules. Automated security patching, often handled by cloud providers for their infrastructure, but also manageable for applications, keeps software up-to-date and protected against known vulnerabilities without manual intervention.
Beyond routine tasks, automation can extend to configuration management, ensuring that security settings across the cloud ERP remain consistent and compliant. Automated threat detection systems can trigger alerts or even initiate containment actions without human oversight, drastically reducing response times to security incidents. In disaster recovery, automated failover mechanisms can switch operations to a redundant system in seconds, minimizing downtime. By reducing manual effort and human error, automation significantly enhances the reliability and effectiveness of security and recovery processes, providing a powerful layer in ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Myth vs. Reality: Debunking Common Cloud Security Misconceptions
Despite the widespread adoption of cloud technologies, many myths about cloud security persist, particularly among small businesses hesitant to move their critical systems like ERP to the cloud. One common misconception is that the cloud is inherently less secure than on-premise solutions. In reality, leading cloud providers invest billions in cybersecurity, employing world-class experts, advanced technologies, and physical security measures that far exceed what most small manufacturers could ever afford or implement on their own. The issue is rarely the cloud itself, but rather its misconfiguration by the user.
Another myth is that moving to the cloud absolves the business of all security responsibilities. This misconception ignores the shared responsibility model. While the provider secures the infrastructure, the customer is ultimately responsible for securing their data within that infrastructure. This includes managing identities, access controls, data encryption keys, and network configurations. Understanding and actively participating in this shared responsibility is crucial. Dispelling these myths is an important step for small manufacturers to confidently focus on proactively ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing.
Conclusion: A Secure and Resilient Future for Small Manufacturing in the Cloud
The journey for small manufacturing businesses towards digital transformation with cloud ERP is filled with immense promise, offering unparalleled opportunities for growth, efficiency, and competitiveness. However, realizing this potential hinges entirely on a proactive and unwavering commitment to ensuring disaster recovery and data security in Cloud ERP for small manufacturing. This isn’t just about implementing a few security tools; it’s about embedding a security-first mindset into every aspect of the cloud ERP strategy, from vendor selection and system configuration to employee training and continuous monitoring.
By understanding the shared responsibility model, carefully vetting cloud providers, implementing robust access controls, establishing comprehensive backup and restoration strategies, and fostering a security-aware culture, small manufacturers can confidently navigate the complexities of the cloud. They can protect their invaluable data, safeguard their operational continuity against unforeseen disruptions, and ultimately build a resilient foundation for sustainable success in an increasingly digital and interconnected world. The future of small manufacturing in the cloud is not just efficient and scalable; with the right strategic focus, it is also incredibly secure and resilient.